How To Set Affinity Rules Vmware
DRS analogousness and anti-analogousness rules aid Distributed Resources Scheduler (DRS) perform better placements of virtual machines by understanding the application dependencies and availability. In this post, I will evidence y'all how to create affinity and anti-affinity rules in the vSphere Spider web Customer, and I volition give some existent-world examples.
- Author
- Recent Posts
![]()
The Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) will automatically residuum the virtual machines (VMs) in the vSphere cluster based on resource usage. Most of the time, DRS does its chore perfectly. But because DRS is not aware of applications running on the VM and its dependencies, we need to help DRS optimize the placement of VMs on ESXi hosts in some cases. Analogousness and anti-affinity rules tin help define the limitations and constraints when it comes to moving VMs.
Creating a VM affinity rule ^
Y'all can create a VM analogousness rule to place a specific grouping of VMs on a single ESXi host. When yous are running a multi-tier application, for instance a web server, an awarding server, and a backend database server, those three tiers communicate intensely. If the tiers are on different ESXi hosts, this will upshot in heavy network traffic betwixt the hosts.
To meliorate performance, we can create an affinity rule to ensure the multi-tier application always resides on the same ESXi host. If you manually move a VM, DRS considers the analogousness rule and migrates the other two VMs to the aforementioned host, or it moves the manually moved VM back to the original host. When providing recommendations, vSphere DRS considers performance optimization.
DRS migrates the VM according to affinity rules if information technology is in automatic mode. When DRS is in partially automated or manual mode, it merely offers recommendations to migrate a VM to comply with the affinity rules.
Log in to vCenter Server using the vSphere Spider web Client. Select the vSphere cluster where y'all want to create VM affinity rules and then click Configure -> VM/Host Rules -> Add together.
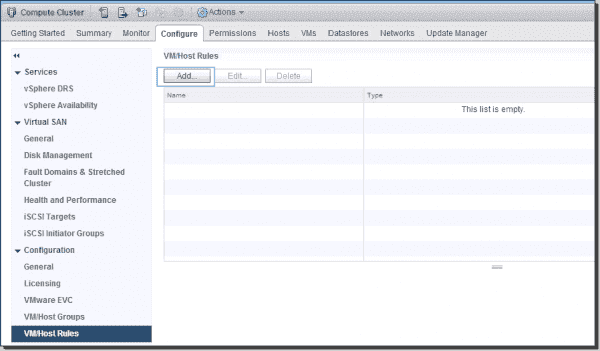
Create a VM analogousness rule in the DRS Cluster
Specify the proper noun for the anti-affinity rule, select Keep Virtual Machines Together from the Type drop-downwards, and click Add.

Select the rule type Keep Virtual Machines Together
Select the VMs from the list, click OK to add VMs to the affinity rules, and click OK to create the analogousness rule.
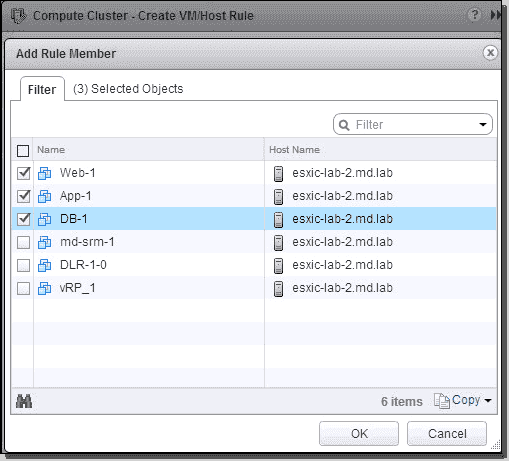
Add VMs to the DRS analogousness dominion
Ensure the Enable Rule checkbox is selected. Click on OK.

Enable the analogousness dominion in the DRS Cluster
This volition create the affinity dominion. You volition exist able to meet the created rules under the VM/Host Rules section of the vSphere cluster.

View analogousness rules nether the DRS cluster
Later on creating the affinity rule, I noticed DRS migrated all three VMs that were role of the analogousness rule into a single ESXi host to comply with the analogousness rule.

VM placement on ESXi hosts afterward the DRS analogousness rule
I tried to migrate one of the multi-tiered application VMs (App-1 in the screenshot in a higher place) to a unlike ESXi host manually. DRS automatically started the migration of two other VMs (DB-one and Spider web-1) to the same host to comply with the affinity rules. Even in a 2d attempt, DRS migrated dorsum the manually vMotioned VM to the same host.
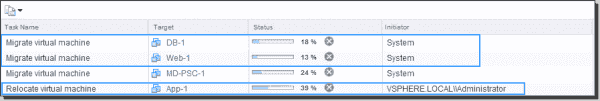
VMware vMotion initiated by DRS affinity dominion
I changed the DRS fashion to partially automated to sympathise the DRS recommendations for affinity rules. The partially automated DRS mode will display the migration recommendation and perform the initial placement when powering on the VM. After changing DRS to partially automatic, I migrated the database VM (DB-1) to a different ESXi host.
Let's run across what DRS recommends in partially automatic mode. To meet the DRS recommendations, select the ESXi cluster -> Monitor -> vSphere DRS -> Run DRS At present, which will manually run DRS immediately. Otherwise, DRS will run every bit per its time interval.
DRS displays the recommendation to migrate the VM DB-i dorsum to the ESXi host where other 2 VMs are running. You lot tin can click on Use Recommendation to apply the DRS recommendation.

View and employ DRS recommendations
Creating DRS anti-affinity rules ^
Anti-affinity rules are just the opposite of affinity rules. You can create an anti-affinity rule to place a specific group of VMs across multiple hosts past separating each VM in the group to run on a different ESXi host. This will improve redundancy.
You can create anti-affinity rules to separate VMs. The unproblematic use case for anti-affinity is when you run a cluster with applications such as Microsoft SQL or Exchange to ensure loftier availability (HA). If the application cluster nodes are running on same ESXi host, you will lose the entire awarding cluster when the host fails.
HA will restart all the application node VMs on a different ESXi host. This means reanimation to the awarding even though you are running a cluster. To avoid this failure, we tin can create anti-affinity rules to separate VMs in the clustered grouping from each other. This volition place each node of the application cluster VMs on different ESXi hosts in the vSphere cluster. Every bit a issue, this provides additional availability along with the application level cluster.
Creating anti-affinity rules works the same way as with affinity rules. The merely difference is to select the type as Separate Virtual Machines instead of Keep Virtual Machines Together.
Specify the name for the anti-analogousness dominion, select Divide Virtual Machines from the Type driblet-down, and then click add. Select the VMs to add to the anti-affinity rule and click OK.
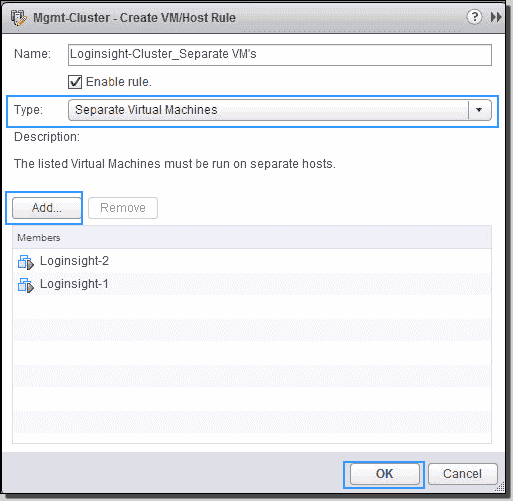
Create a VM anti analogousness rule in the DRS Cluster
After creation of the anti-affinity rule, DRS migrates the VMs to separate ESXi hosts to comply with the rule.
Figure ten. VM placement on the ESXi host after anti-affinity rule creation
Annotation that if your configuration violates DRS rules—say you lot accept three nodes in your cluster merely only 2 ESXi hosts—an error message volition announced under DRS Faults.

View DRS faults in vSphere Web Client
Maintenance style and anti-affinity rules ^
Nosotros accept created anti-affinity rules to split up VMs from each other. We now demand to understand what will happen when we place the ESXi host in maintenance mode. I created an anti-analogousness dominion to separate 2 VMs (Node-1 and Node -2) from each other in a ii-node ESXi cluster.

VM and host view in the DRS cluster
When I try to identify the ESXi host (esxic-lab-1) into maintenance mode, vSphere displays a alarm bulletin:
The following hosts are in a DRS cluster: … One or more virtual machines might need to be migrated to another host in the cluster, or powered off, earlier the requested operation tin can proceed.

ESXi host maintenance manner alert bulletin
The ESXi host is not entering maintenance way fifty-fifty though it is in fully automated DRS manner. It displays another error message:
Unable to automatically migrate the virtual machine Node-1 from the ESXi host esxic-lab-1.
When this happens, yous don't get whatsoever warning or dialog pop-up. You demand to go to the Tasks & Events of the ESXi host manually to understand the reason the host did not enter into maintenance mode.

Related events in ESXi host maintenance mode
In this case, we have to disable the anti-affinity rule temporarily or manually migrate the VM to a unlike ESXi host, thus allowing the host (esxic-lab-1) to enter maintenance mode. As a permanent solution, we can add together an additional host to the cluster.
DRS rules in conflict ^
We can create multiple VM affinity and anti-affinity rules. If two rules are in conflict, you can't enable them. For case, I created an anti-affinity rule to separate the VMs "Loginsight-1" and "Loginsight-ii," and I am trying to create an analogousness rule to keep the same VMs together. This produces an error message:

DRS conflicting rules
The DRS rule is in disharmonize with the existing DRS rules in the cluster. It volition be disabled. The rule tin can be enabled manually when the conflicts are resolved.

View conflicting rules under VM:Host Rules in the DRS Cluster
When two rules conflict, the older 1 takes precedence, and DRS will disable the newer rule. DRS will satisfy the enabled rules and volition ignore the disabled rules. It gives higher precedence to preventing violations of anti-affinity rules than violations of affinity rules.
How To Set Affinity Rules Vmware,
Source: https://4sysops.com/archives/drs-affinity-and-anti-affinity-rules-in-vmware-vsphere/
Posted by: singletontheresurste.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Set Affinity Rules Vmware"
Post a Comment